The browser you are using is not supported. Please consider using a modern browser.
Reading Your Electricity Bill
Table of Contents

Most consumers pay little or no attention to the breakdown of their electricity bill because the numerous sections and costs can make it pretty confusing. However, there are definite benefits to having a closer look at your bill.
Taking the time to do an estimate of your monthly costs for electricity can help you make the right decision on a plan that’s best for your budget and lower your total energy costs.
ElectricityRates.com is committed to helping you manage your energy expenses. This guide provides invaluable information on your energy costs and how power usage affects your overall monthly bill.
How Your Electricity Bill is Calculated
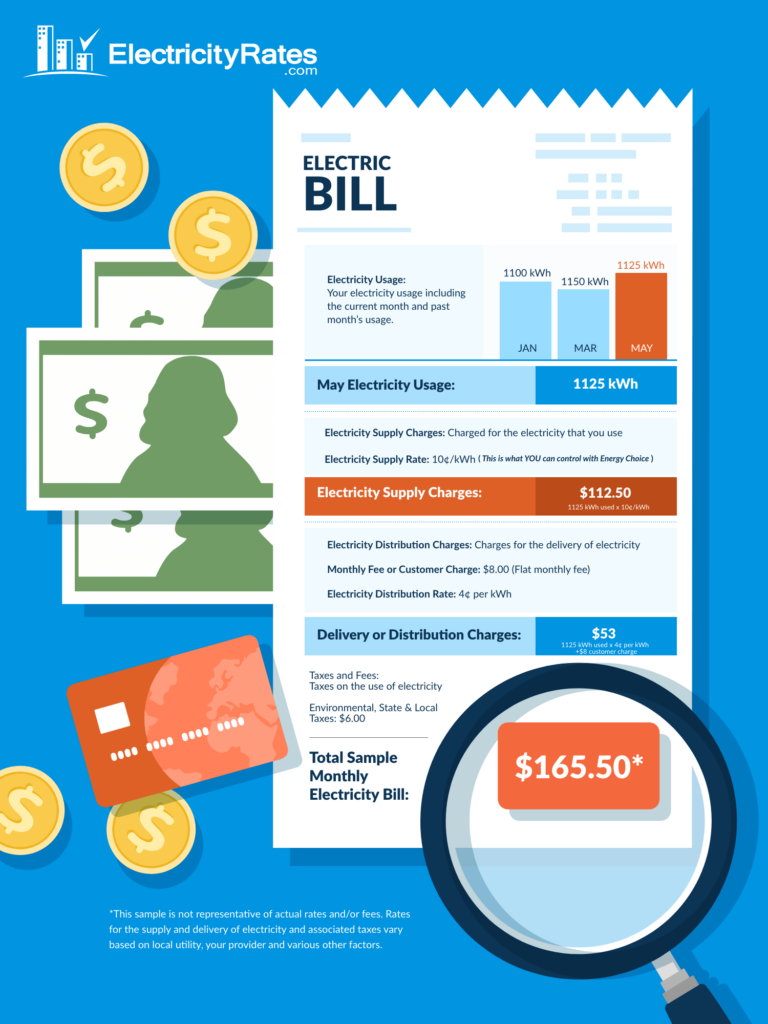
Your electricity bill is typically comprised of the following:
- Electricity Rate – What you pay per kilowatt-hour (kWh)
- Electricity Usage – How much you’re using
- Electricity Charges – How you’re being charged
- Energy Taxes – Taxes on your electricity service
- Additional Charges – Various charges added by your provider or utility
Some utilities also include sections like Usage Profile and Meter Information, which contain details regarding the customer and how the meter information is incorporated into the bill.
Types of Electricity Rate Plans
The rate on your bill represents the amount paid per unit of electricity. Electricity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Typically, you will have one of two types of rate plans: Fixed Rate or Variable Rate.
Fixed-Rate Electricity Plans
Fixed-rate plans allow you to lock in a rate for a specified number of billing cycles. Fixed-rate plans make it easy for you to estimate monthly supply charges and protect you from market price fluctuations.
Variable Rate Electricity Plans
With variable-rate plans, it’s more challenging to estimate monthly supply charges because you pay the current market rate, which can change from month to month.
Understanding Your Electricity Usage
Electricity usage reflects the actual amount of electricity you use during the billing cycle. You can usually determine your usage by looking at past bills. If you’ve recently moved and don’t know what your usage might be, you can try asking neighbors, the landlord or previous residents to get an idea of past electricity or gas usage to determine what your usage might be in the new home.
Electricity Charges
For states and utilities with Energy Choice, electricity bills have two primary components: Supply Charges and Delivery Charges.
Supply Charges
Supply charges (or energy charges) are the charges from your electricity provider for the electricity used in the previous billing cycle.
By default, your utility sets the supply charge based on market rates and conditions. If you participate in Energy Choice and receive your electricity supply from a retail electricity provider, your electricity contract determines the supply rate that you pay for the length of the contract.
To calculate total supply charges, you can multiply your electricity rate by your usage. For example, a customer who uses an average amount of electricity and pays the average utility rate can calculate their approximate utility costs by multiplying those two values:
$0.12 per Kilowatt Hour (kWh) x 908 kWh = $108.96
Delivery Charges Explained
Delivery Charges are the charges by your utility company to maintain the poles, wires and lines that deliver electricity, and to address outages, leaks and other issues related to this equipment. These charges are usually fixed and remain the same every month.
Some utilities also include a Customer Charge. This is a monthly basic distribution charge that covers costs for billing, meter reading, equipment, maintenance, and advanced metering when in use.
Energy Taxes
Taxes, or applicable taxes consist of the estimated total sales tax. This shows what percentage of the bill will go to taxes. Some utilities also include a State Tax Adjustment Surcharge. The state tax adjustment surcharge is a charge or a credit to reflect changes in various state taxes included in the bill. This surcharge often varies by bill component.
If you’ve gone solar or installed other renewable energy systems in your home, you may also be eligible for a renewable tax credit.
Additional Charges On Your Bill
Unfortunately, there are often additional charges added to the customer’s monthly bill that may not be included in their rate. Some companies charge customers for paying their bills online, while others charge for paying by phone. Some companies also charge a monthly fee for not enrolling in their auto-pay option.
Here are more helpful resources about calculating and understanding your electricity bill:
- Calculating Your Electricity Bill
- What is a Kilowatt-Hour?
- Everything You Need to Know about Your Electricity Contract
- When is Electricity the Cheapest?
- Finding Your Supply Rate
- Renewable Tax Credits
Average Electricity Bill
According to the Energy Information Association (EIA), the average American home uses 10,972 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity annually, an average of about 914 kWh per month. Apartments and small homes will typically use less where larger homes with greater energy demands can use upwards of 2000 kWh of electricity per month.
The average electricity bill in the United States is $117.65 per month. Hawaii has the largest average bill at $168.13 per month due to its high average energy rates. Utah has the lowest average bill at $77.25 per month due to a combination of low average rates and average usage.
Lowering Your Electricity Bill
If you live in an area with deregulated energy or “Energy Choice,” you have the ability to choose your provider and secure the best electricity rate and plan for your home. ElectricityRates.com makes it simple to compare rates, find the best one for you and sign up in minutes. All you need is your current utility account information.
Additionally, you can lower your bill by taking an inventory of what’s using the most electricity in your home and cutting back on unnecessary usage.
Here are more helpful resources for comparing rates and lowering your electric bill:
- Lowering your Electricity Bill
- Finding My Account Number
- Comparing Electricity Rates
- Switching Electricity Providers
Electricity Bill Overview by Utility
Find more information about electricity bills for specific utilities below including how to find the Price to Compare, your current supply rate, usage history and more!
- Ameren Bill
- Atlantic City Electric Bill
- BGE Bill
- ComEd Bill
- Con Edison Bill
- Delmarva Power Bill
- Duke Energy Ohio Bill
- Duquesne Light Bill
- Eversource (NSTAR) Bill
- Eversource Connecticut (CPL) Bill
- JCPL Bill
- MA National Grid Electric Bill
- Met Ed Bill
- National Grid Bill
- PECO Bill
- Penelec Bill
- Penn Power Bill
- PEPCO Bill
- Potomac Edison Bill
- PPL Electric Bill
- PSEG Bill
- West Penn Power Bill
- United Illuminating Bill