The browser you are using is not supported. Please consider using a modern browser.
A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Energy
Table of Contents

We live in a world where energy sustainability is no longer just an option but a necessity. And solar energy shines as a beacon of hope. The USA is in the midst of a significant shift towards renewable energy sources, with the U.S. Energy Information Administration declaring that solar energy will supply nearly all energy growth for the next two years.
Homeowners, business owners, and renters across the nation are turning their gaze towards the sun, seeking a cleaner, more sustainable way to power their lives – at a fair price to boot. This transition is not just about embracing green energy. It’s a strong statement of our collective responsibility towards the planet and future generations’ energy security.
Solar energy, with its promise of a cleaner Earth and the allure of energy independence, is capturing the attention of Americans from coast to coast. Read on to learn about the pros and cons of solar energy, what to know about choosing solar energy companies, and how to save money today.
How Solar Panels Work: Harnessing the Sun’s Power
At the heart of the solar revolution are solar panels, marvels of technology that convert sunlight into electricity. But how does solar energy work, exactly? Solar panels are made of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which absorb sunlight and trigger an electric current.
This current is converted from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), powering homes and businesses with the sun’s nearly endless energy. The beauty of solar power lies in its simplicity and efficiency. It provides a direct renewable source of energy that reduces reliance on fossil fuels and slashes our carbon footprint.
The Solar Spectrum: Renewable Energy Production in the U.S.
The U.S. renewable energy landscape is diverse, with solar energy leading alongside wind energy. With new solar projects coming online this year, the EIA forecasts that U.S. solar power generation will grow 75% from 163 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh) in 2023 to 286 billion kWh in 2025. Solar is far outpacing coal and other fossil fuel production in the United States.
This will boost the share of total generation capacity to 5.6% in 2024 and 7.0% in 2025, up from 4.0% in 2023. As we delve into facts about solar energy, it becomes clear that this isn’t just a fleeting trend. Solar power is a substantial pillar of the nation’s energy strategy today and going forward.
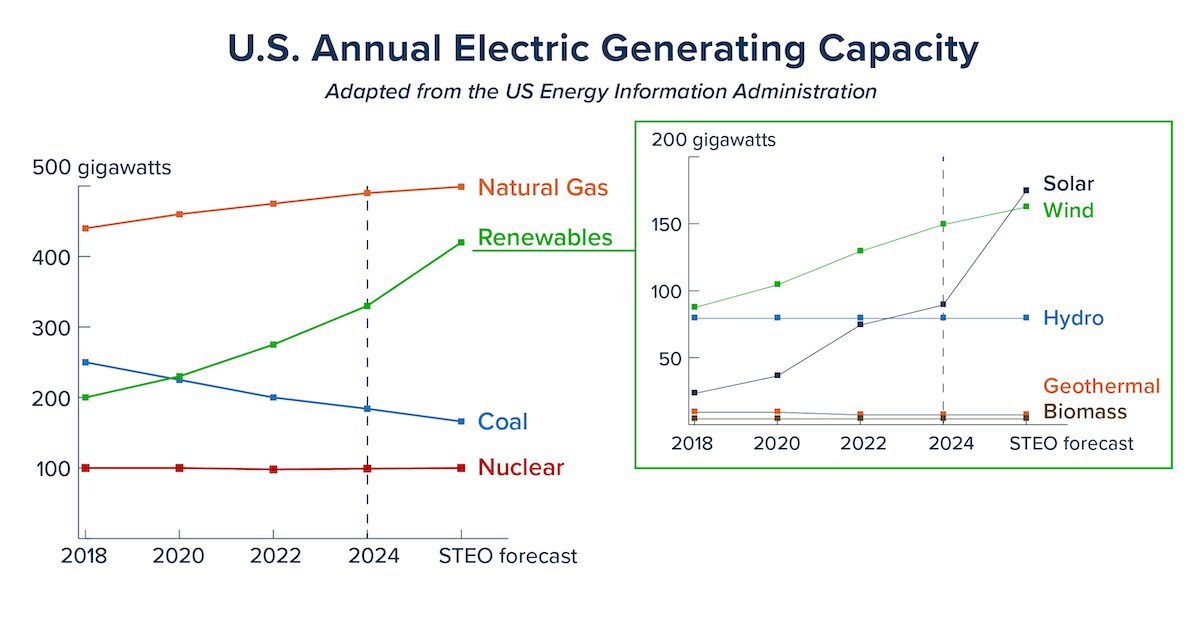
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration
Shining a Light on Solar Options for Your Home
The solar world is full of innovations. Adopting solar power for your home is an excellent way to reduce your carbon footprint, gain energy independence, and lower your electricity bills. Better yet there are varying options to choose from in regard to how you utilize solar to power your home.
Here is a list of key home solar products to consider:
1. Solar Panels (Photovoltaic or “PV” Panels)
These are the most visible part of any solar system. Made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells, solar panels are designed to capture sunlight. When photons from the sun’s rays hit the semiconductive material (usually silicon) in the cells, they knock electrons loose. This movement of electrons creates a flow of direct current (DC) electricity.
How it works: Sunlight hits the panels, and the PV cells convert the solar energy into DC electricity. This DC electricity is then sent down wires to the solar inverter, whose job is to convert DC power into usable AC power for appliances and electronics within your home.
2. Solar Battery Storage
A solar battery allows you to store excess electricity generated by your solar panels for later use. This is particularly useful for grid-tied systems that want to maximize self-consumption and for off-grid or hybrid systems that need backup power.
How it works: During the day when your solar panels are producing more electricity than your home is using, the excess power is sent to the solar battery to be stored. Once the sun goes down or on a cloudy day, the stored energy can be discharged from the battery to power your home, reducing or eliminating the need to pull electricity from the utility grid. In the event of a power outage, the battery can power your home’s “critical loads” (like lights, refrigerators, and Wi-Fi) until the grid is restored.
3. Community Solar
Community solar emerged in the late 2000’s and has picked up massive momentum across the U.S. It allows everyone to benefit from solar power without installing panels or equipment.
How it works Community solar is when a group of people share electricity from a local solar farm. The model that allows multiple customers, such as individuals, businesses, and nonprofits, to benefit from a solar project within a specific region. Customers subscribe to solar panels located off-site. They receive a credit on their electric bill for the electricity produced by the portion of the community solar they own.
4. Retail Electricity Provider: These providers operate in deregulated energy markets where consumers can choose their electricity supplier. They procure electricity from large-scale solar farms and sell it directly to residential and commercial customers.
How it works: When you switch, your electricity provider takes your electricity supply payment and uses it to purchase renewable energy certificates (also known as renewable energy credits, or REC’s) on the behalf of you. Where you physically get your electricity from remains the same. However, now you’re helping offset your energy usage by ensuring more renewable power is entering the grid.
Together, these products offer varying degrees of utilizing sustainable energy system in your home all while minimizing your carbon footprint.
Common Solar Energy Myths vs. Solar Energy Facts (The Truth)
Myth 1: Solar panels do not work in cold, cloudy, or foggy climates.
Fact: Solar panels can still generate power in less-than-ideal weather conditions. They operate most efficiently in sunny conditions, but they can also produce electricity on cloudy or foggy days, and cold weather can actually improve performance by increasing their conductivity.
Myth 2: Solar energy costs are too high and unavailable for most people.
Fact: The price of solar energy installation has significantly decreased over the past decade, making it more accessible and affordable for homeowners and businesses. Additionally, many governments and organizations offer incentives, rebates, and financing options that further reduce the cost of solar installations.
Myth 3: Solar panels require a lot of maintenance.
Fact: Solar panels are relatively low maintenance. They may need occasional cleaning to remove dirt, leaves, or snow that could block sunlight, but generally, they require little upkeep to function efficiently.
Myth 4: Solar energy can only be used during the day.
Fact: While solar panels generate electricity during daylight hours, advancements in solar storage technologies, such as batteries, allow extra energy produced during the day to be stored and used at night, making solar energy increasingly versatile.
Myth 5: Installing solar panels can damage your roof.
Fact: When done correctly by a professional, solar panel installation does not damage your roof. In many cases, solar panels can actually protect the portion of the roof they cover by shielding it from the elements.
Myth 6: Solar panels take more energy to manufacture than they will ever produce.
Fact: Solar panels are designed to generate more energy over their lifetimes than the energy used in their production, transportation, and installation. The energy payback period can vary but is typically a few years. After that, the solar panels continue to produce clean energy, often for 25 years or more.
Myth 7: Solar energy is only for wealthy individuals or the eco-conscious.
Fact: Solar energy has become increasingly mainstream and is for more than just the wealthy or those particularly focused on environmental sustainability. With various financing options and the potential for energy cost savings, solar energy is an economically viable choice for a broad range of individuals and businesses.
Solar energy continues to be an increasingly important part of the global move towards renewable energy sources, offering both environmental and economic advantages.
The Environmental Impact of Solar Energy
Switching to solar isn’t just good for your wallet; it’s a win for the planet.
1. Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Solar energy systems do not produce air pollution, water pollution, or greenhouse gases during operation. This leads to a significant reduction in carbon dioxide emissions compared to fossil fuel-based energy sources.
2. Water Conservation:
Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology uses minimal water, primarily for cleaning panels. A shift to solar could reduce water usage by up to 88% by 2050, compared to traditional thermoelectric power plants that require large amounts of water for cooling.
3. Air Quality Improvements:
The transition to solar energy could lead to substantial improvements in air quality. These improvements are estimated to save $300-$400 billion by 2050 due to reduced health impacts from air pollution.
4. Land Use Efficiency:
While solar installations require land, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory predicts that ground-based solar will only need up to 0.5% of the total land area of the lower 48 states to achieve zero carbon emissions from the electric grid by 2050. For comparison, U.S. agriculture requires 43% of the total U.S. land area.
5. Long-Term Environmental Benefits:
After an initial “energy payback time” of 1-4 years, solar panels operate carbon-neutrally for 86.6% to 96.6% of their typical 30-year lifespan.
Solar energy reduces your carbon footprint, cutting down on greenhouse gas emissions. It’s a step towards a cleaner, more sustainable future, proving that small changes at home can have a global impact.
The Economic Impact of Solar Energy Solutions On Jobs and Industry Growth
Solar is more than fueling sustainable energy. It also surges the U.S. economy forward. The solar industry has been a significant job creator, with jobs increasing nearly 17 times faster than the overall economy in recent years. U.S. solar capacity more than tripled from 40,000 MW in late 2016 to over 135,000 MW by the end of 2022.
The solar industry is a powerhouse of job creation in engineering, manufacturing, sales, installation, research, and more. In 2024, solar is expected to contribute over 60% of new U.S. electricity generation, with a 41% increase in solar electricity generation compared to 2023.
As more Americans embrace solar, the industry continues to grow, fueling innovation and supporting communities nationwide.
The Future Of Solar Energy
Embracing solar energy is more than a trend. It’s a lifestyle choice that benefits you, your local community, and the planet. As we move towards a cleaner, greener future, solar energy stands out as a path of hope and progress. For homeowners, business owners, and renters across the USA, the solar era is here, promising a better future for the environment and our wallets.