The browser you are using is not supported. Please consider using a modern browser.
Options for Energy Assistance with Your Electricity Bill
In recent times, the electricity industry has seen significant shifts, leading to a rise in electricity costs across the United States. These changes are multifaceted, involving increased demand, transitioning energy sources, regulatory changes, and infrastructural upgrades. Understanding these dynamics and where costs are highest can empower consumers to seek assistance effectively.
Table of Contents

Why Are Electricity Costs Rising?
There are numerous reasons for rising electricity costs. Here are some of the major causes.
Increased Demand
As our world becomes more digital, the electricity demand has surged. This is not only due to population growth but also the proliferation of electronic devices and electric vehicles.
Transition to Renewable Energy
Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources is necessary for environmental sustainability but comes with initial costs. Investment in new technologies and infrastructure can lead to higher electricity rates in the short term.
Infrastructure Upgrades
Many parts of the electricity grid are outdated and require modernization to ensure reliability and accommodate new energy sources. These upgrades are costly and often passed on to consumers.
Regulatory Changes
Policies and regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions can also contribute to rising costs as utilities invest in cleaner, but currently more expensive technologies.
Top 10 States with the Highest Electricity Rates
The states with the highest electricity rates often have specific circumstances contributing to their elevated costs. Factors include reliance on imported energy, state-level regulations, and the availability of natural resources. As of 2023 (the last full year of data), here are the top ten states known for higher electricity costs, including their average rate in terms of cents-per-kilowatt-hour:
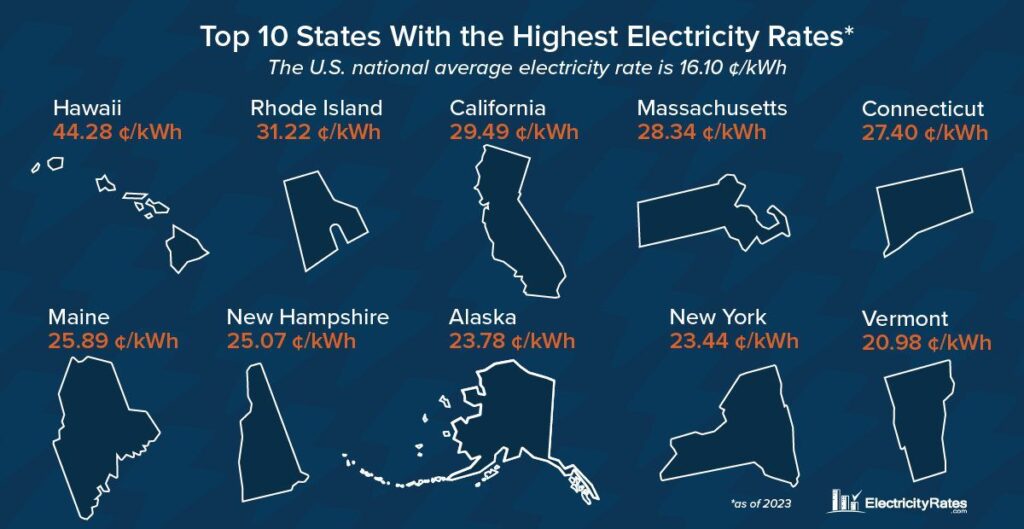
These states exemplify the complex interplay of factors contributing to higher electricity costs, from geographical challenges to policy decisions favoring long-term sustainability over short-term affordability.
Federal Assistance Programs
Whether you live or work in one of the states mentioned above, electricity can be a necessity that is challenging to afford. For those struggling to manage rising electricity bills, several federal assistance programs offer relief:
Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP)
LIHEAP provides financial assistance to eligible low-income households to manage costs associated with heating and cooling homes, bill payment assistance, energy crisis assistance, weatherization, and energy-related home repairs.
LIHEAP not only helps with managing heating and cooling costs but also significantly impacts families’ well-being by preventing energy-related health risks. This assistance enhances living conditions by ensuring homes remain warm during winter and cool during summer, thereby reducing health problems associated with extreme temperatures.
For more information about LIHEAP benefit levels according by state, you can refer to their Benefit Levels for Heating, Cooling and Crisis chart.
Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP)
WAP helps low-income families improve energy efficiency and reduce energy bills by making their homes more energy-efficient. Services may include insulation, air sealing, and installing energy-efficient appliances.
By improving home energy efficiency, WAP not only reduces energy bills but also contributes to environmental sustainability. The program’s impact extends beyond immediate financial relief, promoting healthier living environments and prolonging the lifespan of housing for low-income families, which in turn can help to stabilize vulnerable communities.
For more details on just how much money and energy can be saved through WAP, refer to this fact sheet by the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Block Grant Program (EECBG)
EECBG supports projects that improve energy efficiency, reduce energy use and fossil fuel emissions, and create green jobs. However, this program is not for individuals. Like the SEP grants above, this program indirectly benefits individuals by improving the energy efficiency of community facilities which can lead to reduced public energy expenditures and more environmentally friendly communities. Only local governments, states, and tribes can apply for funding.
Examples of projects created with EECBG support include
- Installing onsite renewable energy technology like solar panels, wind turbines, and biomass energy systems in government buildings and local communities
- Reducing the energy used in transportation, such as by improving public transit facilities, adding bike lanes, and promoting energy-efficient city planning
- Implementing advanced energy distribution technologies such as smart grid applications and district heating and cooling systems has been another area of focus
- Conducting energy audits on buildings and using the findings to implement energy efficiency improvements
In certain cases, your local government, state or tribe may use EECBG funds to create programs, like rebates or other incentives to implement green technologies, for which you can directly apply.
Rural Energy for America Program (REAP)
REAP offers financial assistance, in the form of guaranteed loan financing or grants, to agricultural producers and rural small businesses to purchase and install renewable energy systems and improve energy efficiency.
REAP not only assists in the adoption of renewable energy and energy efficiency improvements but also bolsters the economic resilience of agricultural communities. By reducing energy costs, the program helps ensure that businesses can invest more resources back into the local economy and maintain the viability of rural areas.
With the passage of the Inflation Reduction Act, more than $2 billion has been earmarked for REAP through 2031.
Check out financial assistance options through REAP for program information and how to submit an application.
State Energy Program (SEP)
SEP provides grants to states to assist in designing, developing, and implementing renewable energy and energy efficiency programs. This leads to localized solutions for energy challenges, with research showing that for every $1 spent in SEP grants, $4.50 is reaped in energy cost-savings.
SEP not only aids in reducing state-wide energy costs but also supports the national goal of achieving energy independence, thereby enhancing overall community resilience against energy price fluctuations.
SEP grants don’t go directly to individuals. The federal government passes it to state governments who then choose how to allocate it. However, states may choose to make funds available to residents in the form of incentive programs. Check your state government’s energy-related websites to find out how they’re using their SEP money.
Some examples of projects funded via the SEP include . . .
1. Alabama: Through the SEP, Alabama expanded its Wastewater Energy Management Initiative, resulting in significant annual electricity savings and reduced nitrogen pollution in waterways.
2. California: SEP funds supported the development of new appliance standards and bolstered grid resilience, contributing to substantial energy savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions over several years.
3. Minnesota: In Minnesota, SEP partnerships have led to massive energy savings through building designs that adhere to the state’s Sustainable Buildings 2030 standards.
4. Rhode Island: SEP-funded projects have significantly contributed to the state’s clean energy workforce growth and the expansion of Rhode Island’s clean energy portfolio.
5. Texas: Texas used SEP funds to leverage millions in capital for clean technology startups, demonstrating the program’s ability to drive economic impact and job creation in the clean energy sector.
6. West Virginia: SEP funds in West Virginia have been utilized to train student engineers who provide no-cost technical assistance to public and private sector clients, identifying millions in energy cost savings.
For a high-level overview of the impact of SEP grants since 2010, visit this U.S. Department of Energy webpage.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Block Grant Program (EECBG)
EECBG supports projects that improve energy efficiency, reduce energy use and fossil fuel emissions, and create green jobs. However, like SEP above, this program is not for individuals. Only local governments, states, and tribes can apply for funding. Those groups, in turn, may use the funds to benefit you. Check with your local, state, or tribal government for additional energy assistance programs that may help you.
These programs are designed to alleviate the financial burden of energy costs, particularly for vulnerable and low-income households. They not only offer immediate financial relief but also contribute to long-term sustainability by promoting energy efficiency and renewable energy use.
Conclusion
Rising electricity costs are a multifaceted issue influenced by demand, energy transitions, and regulatory frameworks. While some states face higher rates due to specific challenges, federal assistance programs are crucial in supporting those in need. By understanding both the causes of rising costs and the available assistance, consumers can better navigate the complexities of the electricity industry and find ways to manage their energy expenses effectively.
Whether you qualify for federal assistance or not, there’s no reason not to have the best electricity rate. ElectricityRates.com makes that easy to find. Simply use our marketplace by plugging in your zip code or talk to one of our advisors to find the best energy plans for your business.
